- Consulting
- Consulting
Study of the relationship between bats, wind turbines and forests
- Skills Chiropterological expertise, statistical analysis
- Completed 2023
- Location Walloon region
- 3 different missions to answer the same question
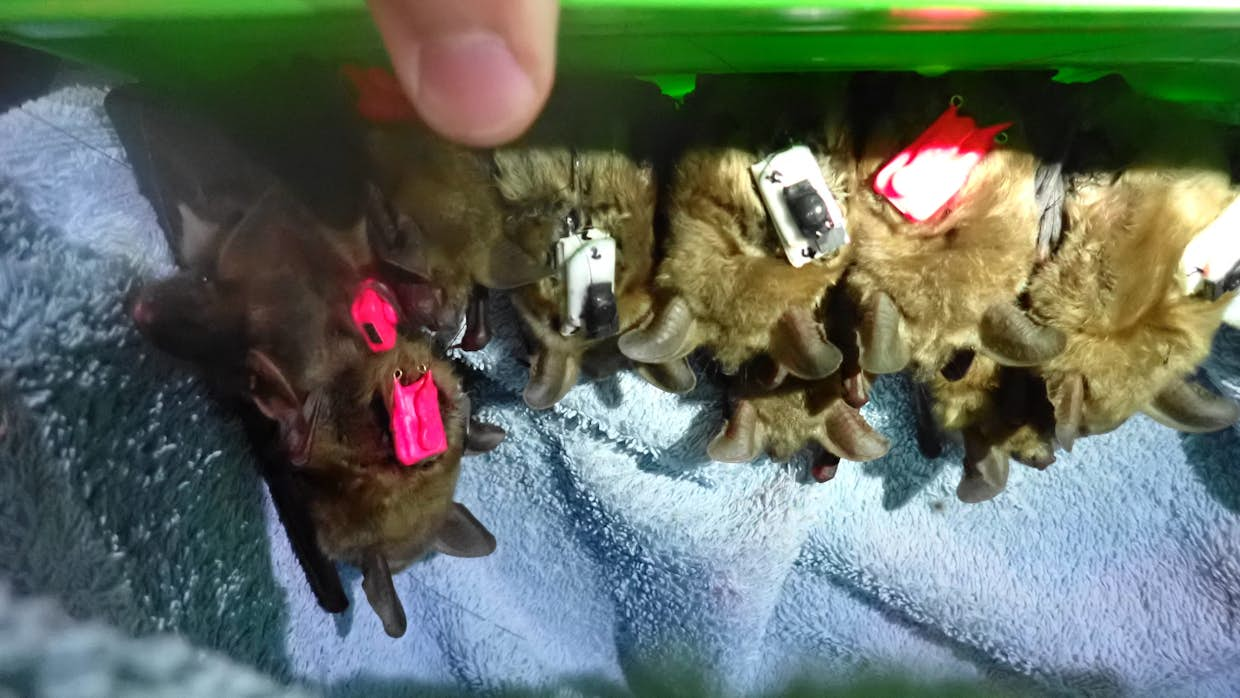
- 24 Greater Mouse-eared Bats (from 2 colonies) equipped with GPS tags
- 55,000 acoustic data to produce predictive map
- 20 environmental impact studies fed into a multivariate analysis
The SPW (DEMNA) has entrusted to Ecofirst a study in order to better understand the relationship between bats (and in particular the Greater Mouse-eared Bat) and wind turbines in or near forests. The contract is divided into 3 parts, 2 of which will be carried out jointly with CSD ingénieurs.
This study of bat activity and mortality on forest wind farms in Wallonia is structured as follows:
- A study of the spatial use (including flight altitude) of the Greater Mouse-eared bat, using GPS tags.
- The generation of presence probability maps for different bat species sensitive to wind turbines, using natural habitat modelling based on existing acoustic data.
- An analysis of the risks associated with reducing the distance between the wind turbines and the forest edge, and between the blade tip and the vegetation.
Our expertise at the service of this project:
- Capture and telemetric survey of bats: P. Nyssen and JF. Godeau
- Fieldwork organization and external contacts: P. Nyssen
- GPS data analysis: JF. Godeau
- Literature review: P. Nyssen and JF. Godeau
- Cartographic and statistical analysis: JF. Godeau
For further information: